2:
Intelligence-lab
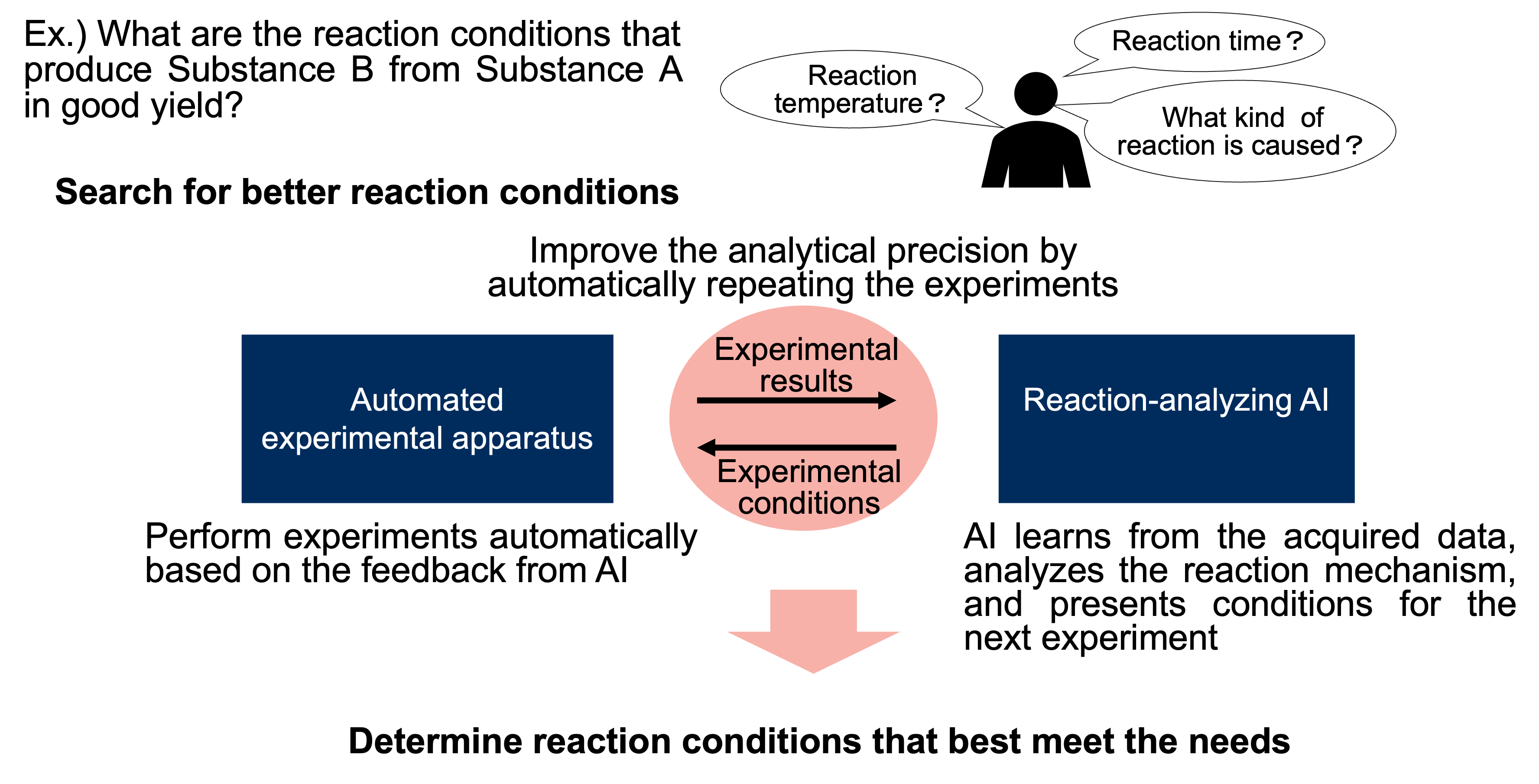
What is to be achieved with this technology
A combination of automated experimental system and reaction-analyzing AI has made it possible to determine reaction conditions that best meet a customer’s needs
Practical example: Reaction experiment/analysis of a gaseous substance
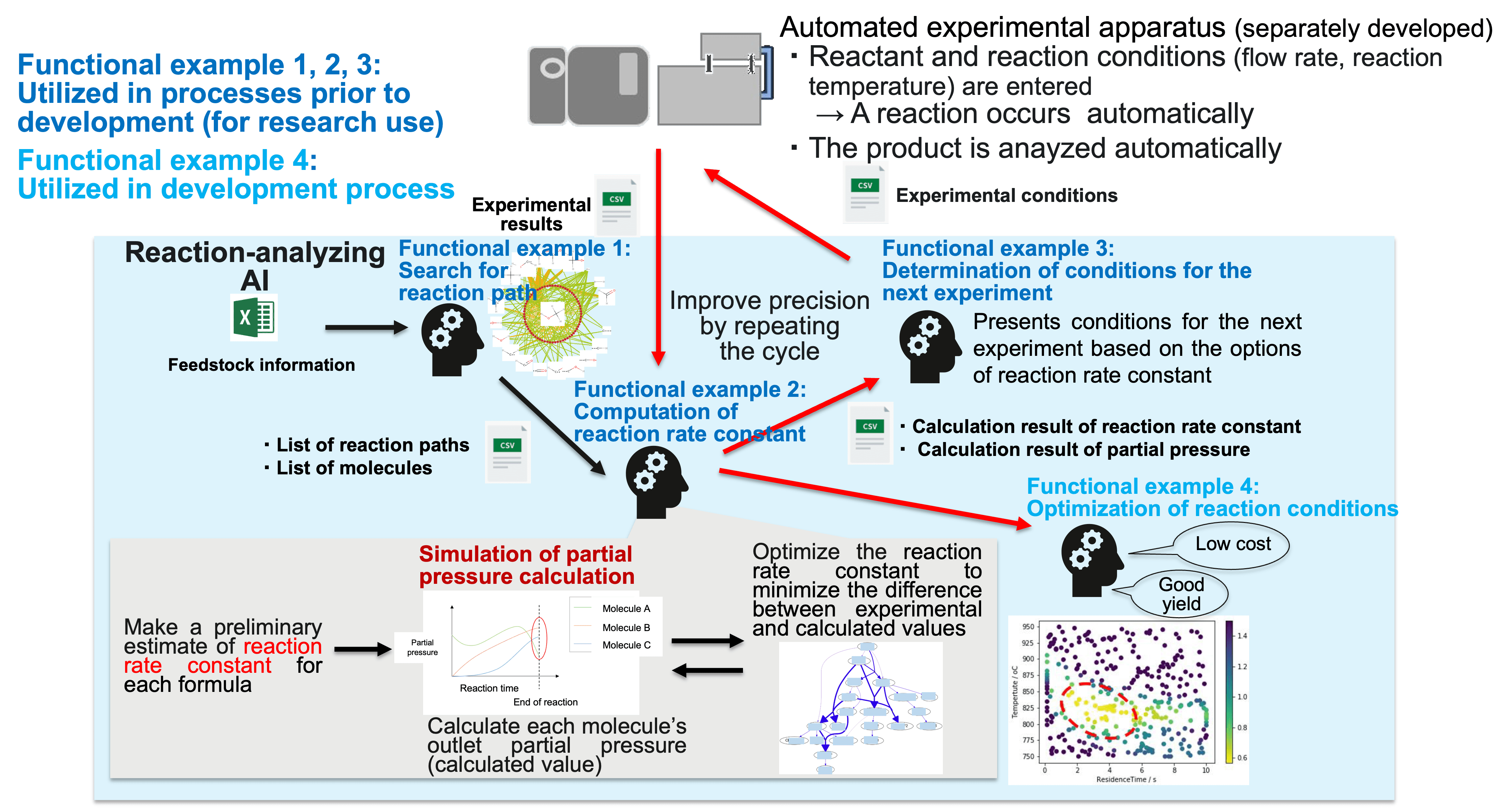
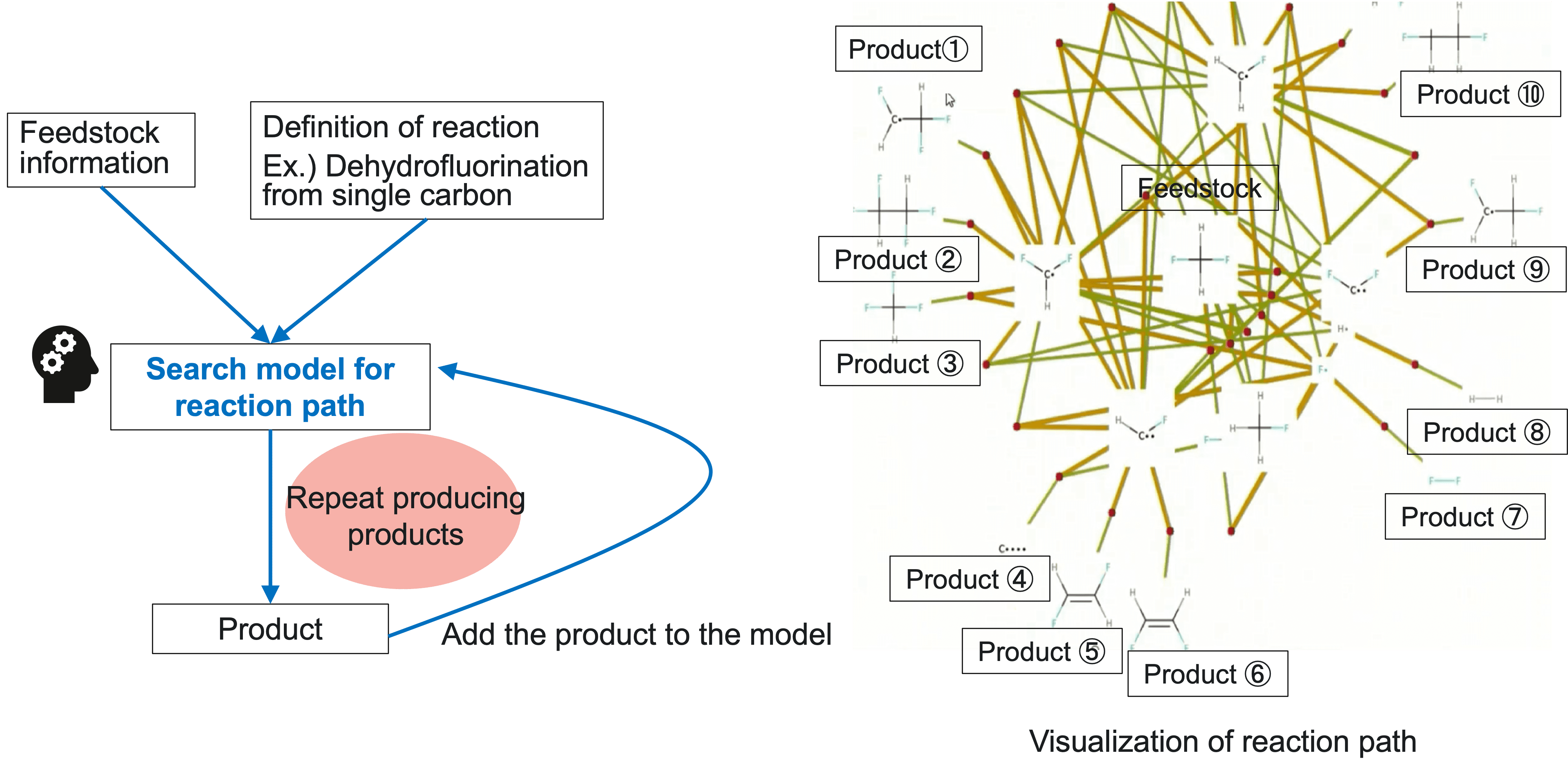
Functional example1:Search for reaction path
By inputting the information of reacting feedstock and definition of reaction into the model, all possible reaction formulas can be searched at once and their paths are visualized.
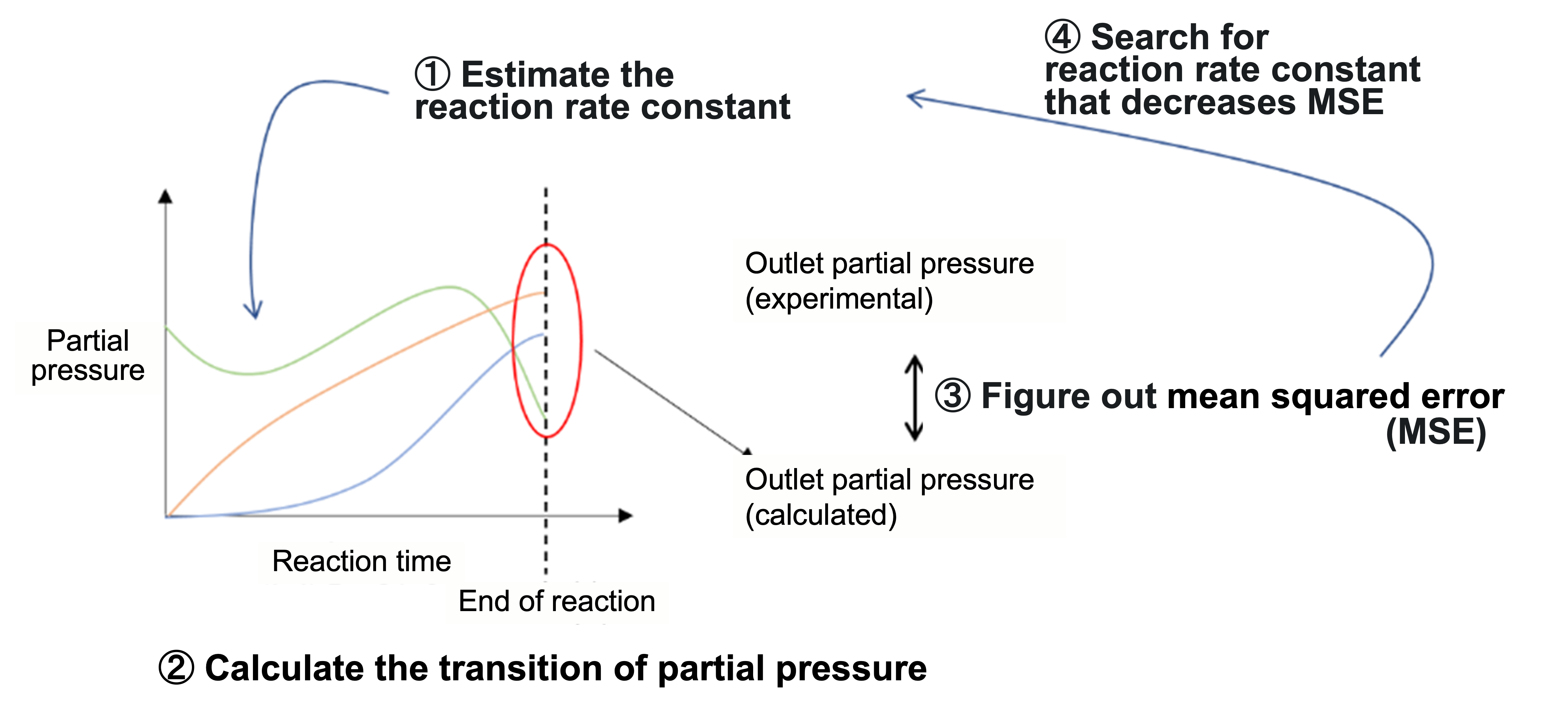
Functional example 2:Computation of reaction rate constant
Search for reaction rate constant for every reaction formula at once
Make a preliminary estimate of reaction rate constant for each formula, and calculate the transition of partial pressure
Figure out the difference between experimental and calculated values of outlet partial pressure, and optimize the reaction rate constant to minimize the difference
Functional example 3: Determination of conditions for the next experiment
Present experimental conditions that can effectively narrow down the options of reaction rate constant computed in Functional example 2, with a small number of experiments
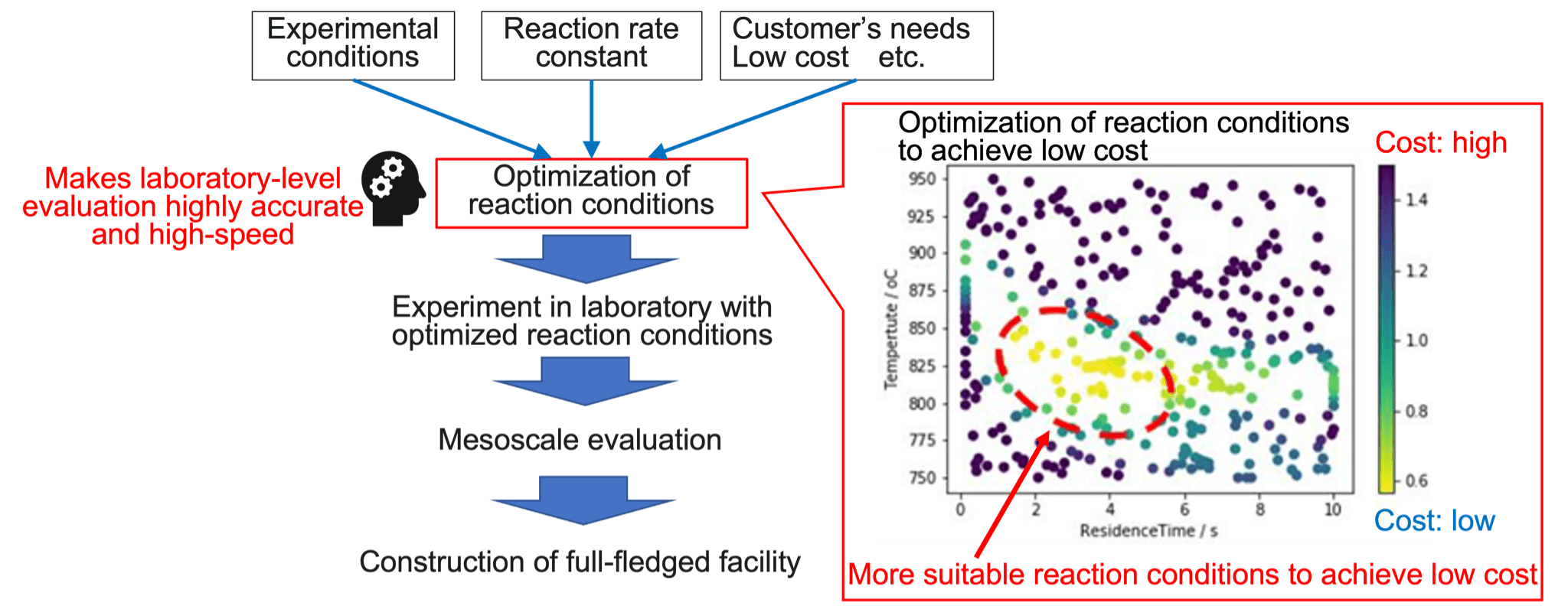
Functional example 4:Optimization of reaction conditions
Estimate post-reaction partial pressure using reaction rate constant and experimental conditions that have been determined through Functional examples 1~3, and then determine “more suitable reaction conditions” that meet customer’s needs using Bayes’ optimization
Bayes’ optimization:an approach to determine parameters that maximize (minimize) an objective function