1:
Toxicity evaluation of iPS cells
What is to be achieved with this technology
Gaseous substances require special toxicity tests which take both time and money. We have been working on the development of simplified toxicity evaluation method for gaseous compounds in order to speed up the toxicity screening process for new compounds.

iPS cells are used for cardiotoxicity and neurotoxicity (narcotic) tests. As for hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and respiratory toxicity, we have developed testing methods using cultured cells for such reasons that their iPS cell-derived cells are not steadily available or they do not match living bodies.
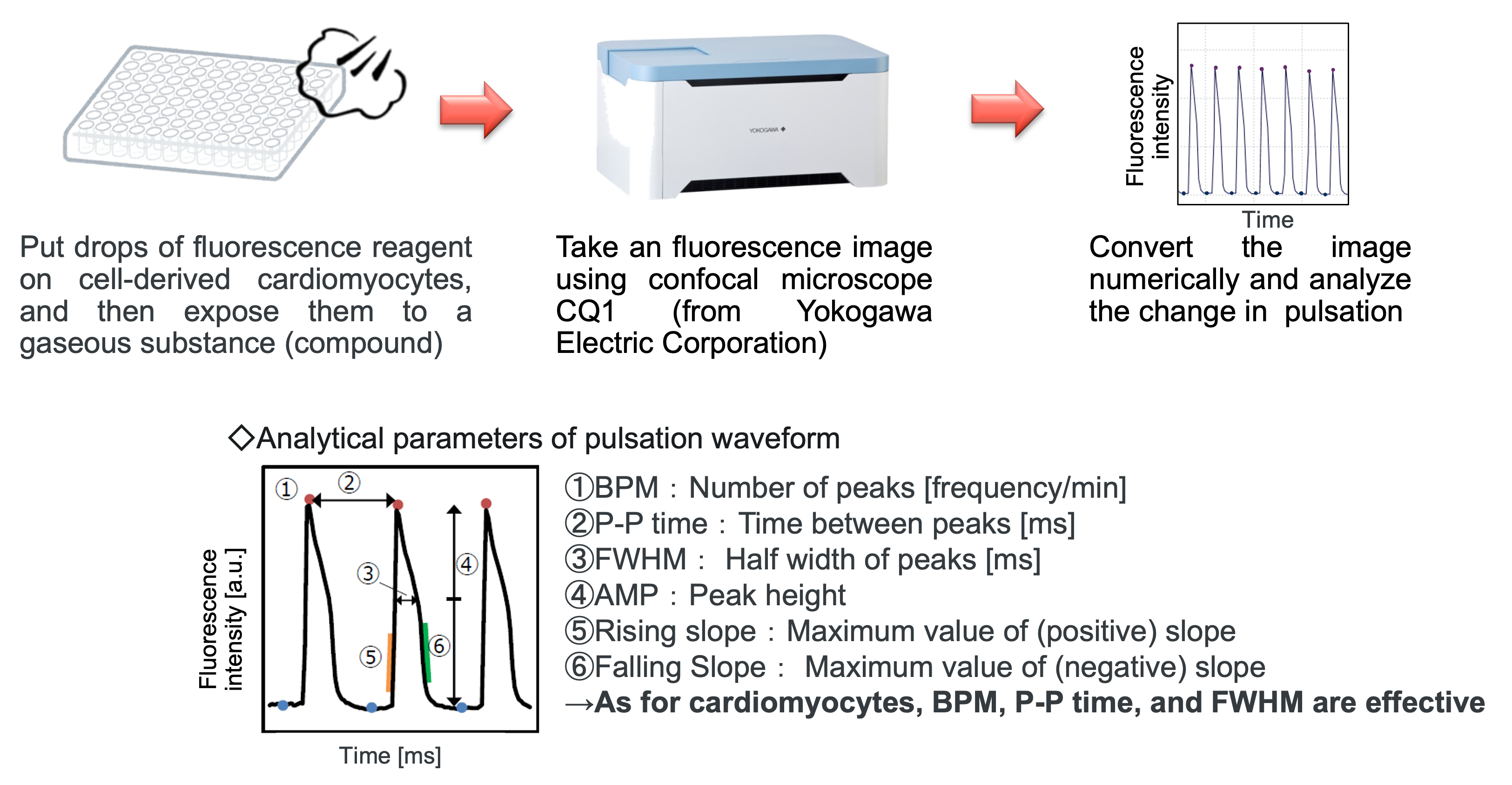
ical example: Gaseous (compound) exposure of iPS cell-derived (cardiomyocytes ⇒ Image analysis)
Influence of a gaseous compound on cardiomyocyte pulsation can be evaluated. Add fluorescence reagent on cardiomyocytes, observe their pulsation using confocal microscope, and visualize the pulsation by image analysis.
Practical example: Cardiotoxic mechanism
We have focused on pulsation of cardiomyocytes as a parameter to be detected.
Ions Na+, K+, Ca2+ are known to be involved in contract and relax of heart muscle.
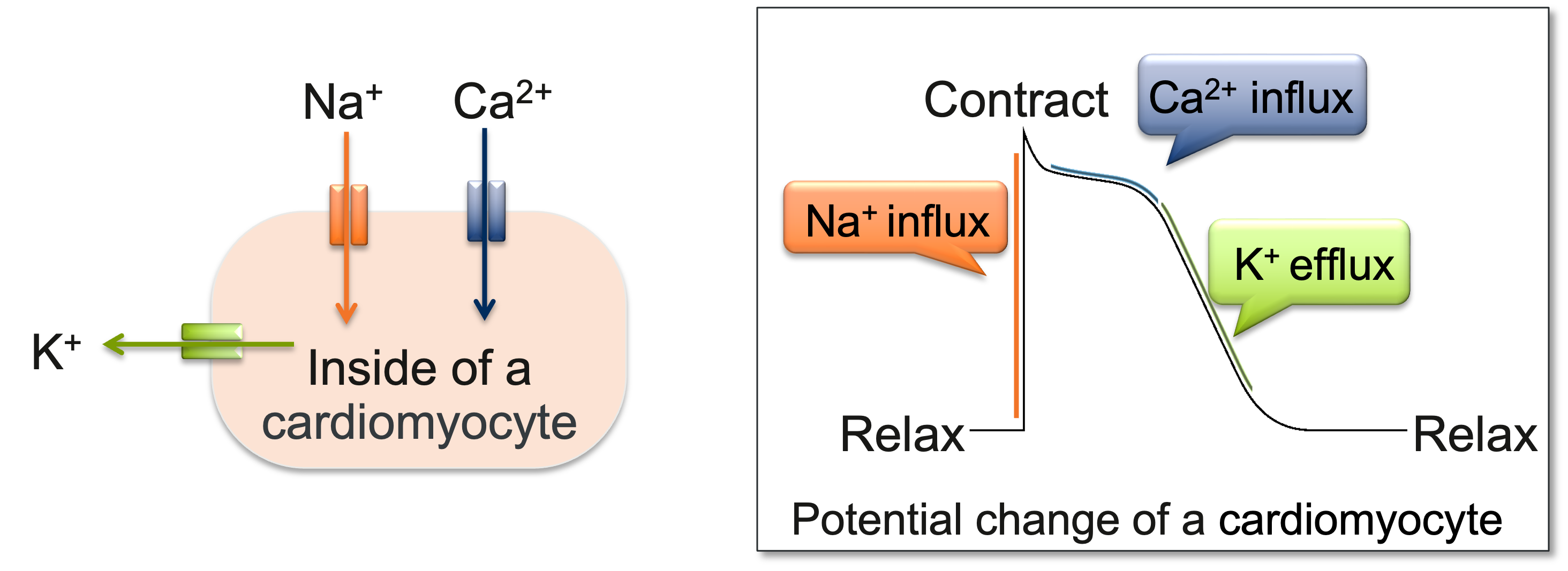
Change in Ca2+ concentration inside of a cardiomyocyte can be observed by adding drops of Ca2+ indicator. We evaluated the influence of gaseous compounds on pulsation of cardiomyocytes.
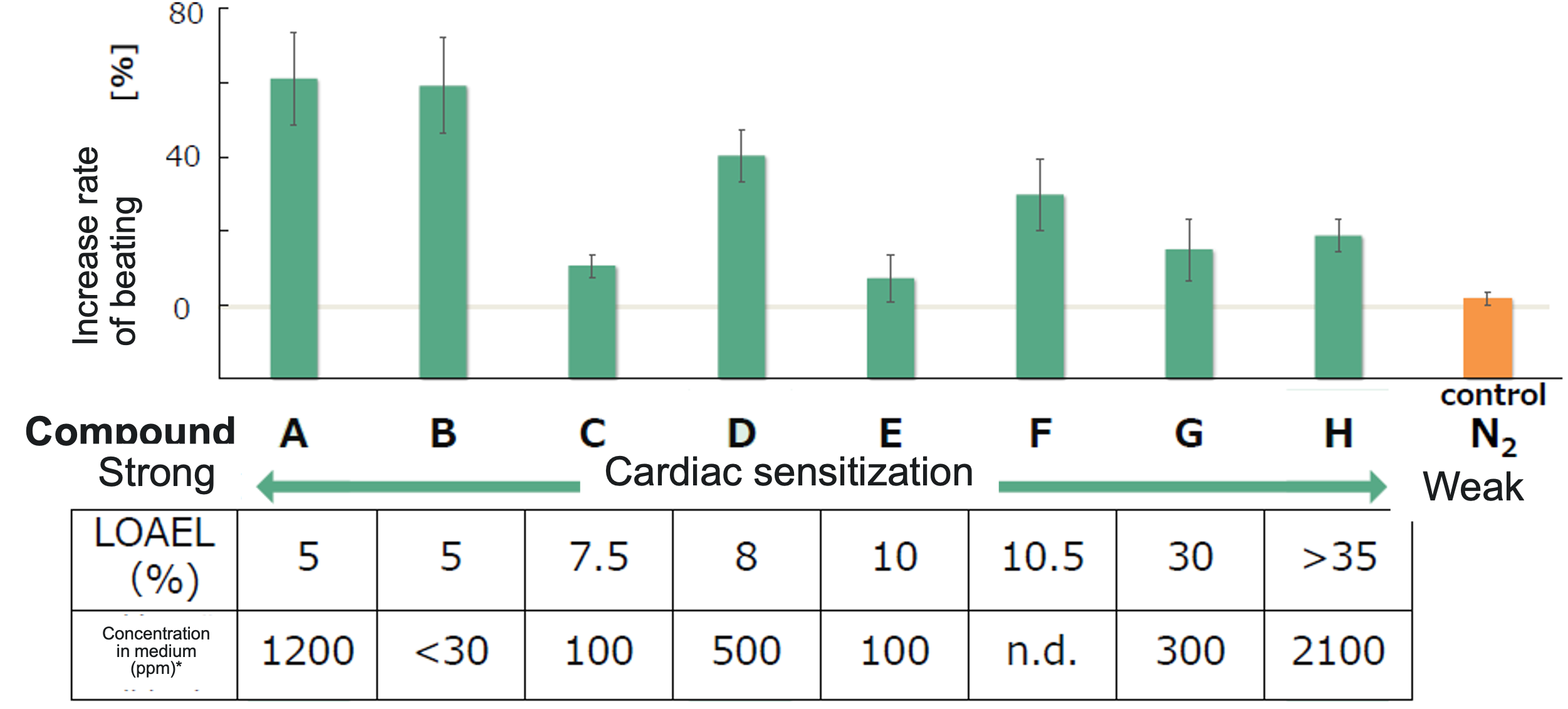
Practical example: Evaluation results of cardiotoxicity
We exposed iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes to eight different types of gaseous compounds that are known to have cardiac sensitization, and we evaluated the degree of their sensitization based on the change in beating rate of the cardiomyocytes. In consequence, LOAEL in cardiac sensitization decreases (i.e. toxicity enhances) as change rate of beating increases.
As for gaseous compound C and E, their effects might not appear due to their low concentration in medium, or species difference (dog vs. human) might be affecting the result.